Main
» Science
· Instrument
· Analysis
· Results
· Publications
· Team
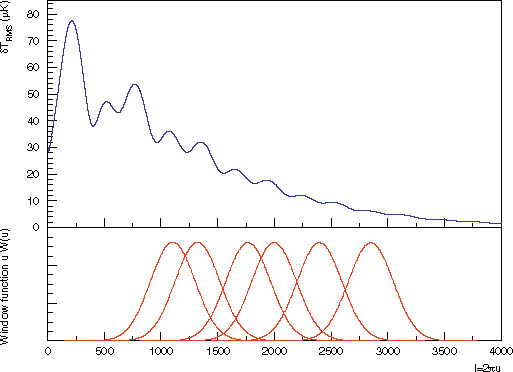
fig 1 The top window is the output of CMBfast with lambda=.7 baryons=.045 cdm=.255 h=.82 and tilt=1. The bottom window shows the window functions for current locations of the antennae. eps
MINT is a small, tightly packed interferometer. Because of the high frequency, MINT still achieves relatively small angular resolution. The design goal was to achieve a minimum l of 1000, approximately where MAP leaves off. This minimum distance also sets the size of the primary reflectors. MINT is tightly packed to maximize the signal. A side effect of tight packing is broad window functions.
The first phase of MINT will measure the damping tail of the anisotropy spectrum of the cmb. Because of the broad l coverage for each window function, MINT's primary goal is to measure the damping envelope. The damping tail probes the photon diffusion scale at the decoupling epoch. The diffusion scale is determined by the thickness of last scattering surface or the duration of recombination and by the baryon content. The angular size of the diffusion scale today measures the curvature of the universe.
check out: